Sleep Apnea Unmasked: 7 Basic Power-Packed Solutions for Peaceful & Better Sleep
Overview
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep. These interruptions can last for a few seconds to minutes and may occur multiple times throughout the night. It can lead to disrupted sleep, fatigue, and other health issues. There are three main types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea, central sleep apnea, and complex sleep apnea syndrome. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage this condition and improve overall sleep quality.
7 Power-Packed Solutions for Peaceful Sleep
-
Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends, to regulate your body’s internal clock and promote better sleep.
-
Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in calming activities before bed, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing.
-
Optimize Your Sleep Environment: Make your bedroom conducive to sleep by keeping it dark, quiet, and cool. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows for optimal support.
-
Limit Screen Time before Bed: Avoid using electronic devices such as smartphones and laptops before bedtime, as the blue light emitted from screens can disrupt sleep.
-
Watch Your Diet: Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime. Instead, opt for a light snack if you’re hungry, and limit liquids to reduce the need for nighttime bathroom trips.
-
Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity, but avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it may interfere with falling asleep.
-
Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or journaling to calm the mind and promote relaxation before sleep.
By incorporating these power-packed solutions into your daily routine, you can improve the quality of your sleep and enjoy a more peaceful rest each night.
Introduction:

Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breathing during sleep, leading to disrupted sleep patterns and reduced oxygen levels in the body. These pauses in breathing, called apneas, can last for a few seconds to a couple of minutes and can occur multiple times throughout the night.
Sleep apnea can have a significant impact on the quality of life, as it can lead to excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty concentrating, and other health issues. It is important to understand the symptoms, causes, and available treatments for sleep apnea to effectively manage this condition and improve overall well-being.
Understanding Sleep Apnea:
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is characterized by interruptions in breathing during sleep, leading to fragmented sleep patterns and decreased oxygen levels in the body. These interruptions, known as apneas, can occur repeatedly throughout the night and can have significant consequences for overall health and well-being.
Sleep apnea can be classified into several types, with the most common ones being obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA). Understanding the different types of sleep apnea is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What is Sleep Apnea?

Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated pauses in breathing or shallow breathing during sleep. These pauses, or apneas, can last for several seconds and may occur numerous times throughout the night. When breathing is interrupted, the brain briefly wakes the individual to restore normal breathing. However, these awakenings are often so brief that individuals may not be aware of them, leading to disrupted sleep.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common type of sleep apnea. It occurs when the muscles in the throat fail to keep the airway open, despite effort to breathe. The resulting blockage leads to loud snoring, gasping, or choking as the individual struggles to breathe.
Central sleep apnea (CSA) is less common and involves a failure of the brain to transmit proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. In this case, the airway is not blocked, but the brain fails to send the necessary instructions for breathing, resulting in pauses in breathing during sleep.
Sleep Apnea Definition
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repetitive pauses in breathing or shallow breathing during sleep. These pauses, known as apneas, can last for several seconds and can occur multiple times throughout the night. Sleep apnea disrupts normal sleep patterns, leading to fragmented sleep and potential health complications.
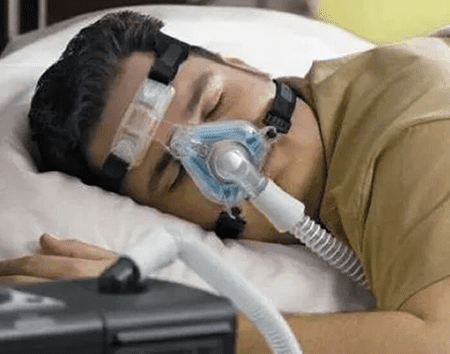
Types of Sleep Apnea
-
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): OSA is the most common type of sleep apnea, accounting for approximately 84% of cases. It occurs when the muscles in the throat relax and block the airway during sleep. The blockage results in shallow breathing or complete pauses in breathing, leading to fragmented sleep and reduced oxygen levels in the body.
-
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): CSA is a less common type of sleep apnea, accounting for about 15% of cases. It occurs when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. Unlike OSA, there is no physical blockage in the airway. Instead, the pauses in breathing are caused by a lack of respiratory effort.
-
Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome (CompSA): Also known as mixed sleep apnea, CompSA is a combination of both obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea. It starts with symptoms similar to OSA but transitions into central sleep apnea over time. This type of sleep apnea requires careful diagnosis and management.
-
Positional Sleep Apnea: Positional sleep apnea is a type of sleep apnea where breathing pauses occur primarily when an individual sleeps in certain positions, such as on their back. Changing sleep position can often help alleviate the symptoms.
-
Mixed Sleep Apnea: Mixed sleep apnea involves a combination of obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea. It can be challenging to diagnose and requires comprehensive evaluation and treatment.
Understanding the different types of sleep apnea is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect you or a loved one may be experiencing sleep apnea symptoms.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can present a range of symptoms that vary in severity from person to person. Here are some common symptoms associated with sleep apnea:

-
Loud and persistent snoring: One of the hallmark symptoms of sleep apnea is loud and chronic snoring. The snoring is often interrupted by pauses in breathing or gasping for air.
-
Excessive daytime sleepiness: People with sleep apnea often experience excessive daytime sleepiness, regardless of the amount of sleep they get at night. This persistent fatigue can interfere with daily activities, work performance, and overall quality of life.
-
Morning headaches: Waking up with headaches is a common complaint among individuals with sleep apnea. The frequent interruptions in breathing during the night can cause decreased oxygen levels, leading to headaches upon waking.
-
Difficulty concentrating and memory problems: Sleep apnea can impair cognitive function, making it challenging to concentrate, focus, and remember things. This cognitive impairment can affect work performance, academic achievement, and daily tasks.
-
Frequent awakenings during the night: Sleep apnea disrupts normal sleep patterns, causing frequent awakenings throughout the night. These awakenings may be accompanied by a choking or gasping sensation as the body tries to restore normal breathing.
-
Dry mouth or sore throat: Breathing through the mouth due to blocked nasal passages or airway obstruction can result in dry mouth or a sore throat upon waking.
-
Irritability and mood changes: Sleep deprivation caused by sleep apnea can lead to irritability, mood swings, and an overall decrease in emotional well-being.
It is important to note that not all individuals with sleep apnea experience every symptom mentioned above. Additionally, some symptoms may be more prevalent in certain populations, such as adults or children.
Sleep Apnea in Adults
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that can affect individuals of all ages, including adults. In adults, sleep apnea is most commonly classified as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). It occurs when the muscles in the throat relax and block the airway during sleep, leading to pauses in breathing.
Here are some specific characteristics and considerations regarding sleep apnea in adults:

-
Risk factors: Certain factors increase the risk of developing sleep apnea in adults. These include obesity, excessive weight gain, smoking, alcohol consumption, family history of sleep apnea, and the presence of other medical conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart disease.
-
Gender differences: Men are more likely to be diagnosed with sleep apnea than women. However, women may develop sleep apnea during pregnancy or after menopause due to hormonal changes and weight gain.
-
Symptoms: The symptoms of sleep apnea in adults, as mentioned earlier, can significantly impact daily life and overall well-being. If left untreated, sleep apnea in adults can increase the risk of developing other health conditions such as hypertension, stroke, and cardiovascular disease.
-
Diagnosis: To diagnose sleep apnea in adults, a sleep study or polysomnography may be conducted. This involves monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep, including brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, and breathing patterns.
-
Treatment options: Treatment for sleep apnea in adults may vary depending on the severity of the condition. Lifestyle changes such as weight loss, regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol and sedatives may be recommended. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy is often prescribed, which involves wearing a mask that delivers pressurized air to keep the airway open during sleep. In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary.
It is crucial for adults experiencing symptoms of sleep apnea to seek medical evaluation and treatment to improve sleep quality, overall health, and quality of life.
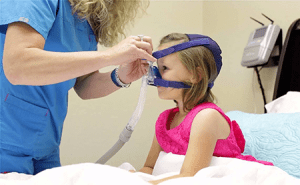
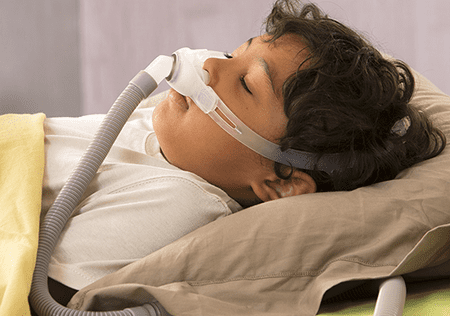
Sleep Apnea in Children
Sleep apnea can also affect children, although the symptoms and causes may differ from those seen in adults. Sleep apnea in children is often categorized as pediatric obstructive sleep apnea (POSA). It occurs when the airway becomes partially or completely blocked during sleep, leading to disrupted breathing patterns.
Here are some key points to understand about sleep apnea in children:
-
Causes: In children, sleep apnea is commonly caused by enlarged tonsils or adenoids, which can obstruct the airway during sleep. Other factors that may contribute to sleep apnea in children include obesity, craniofacial abnormalities, neuromuscular disorders, and certain medical conditions.
-
Symptoms: Children with sleep apnea may exhibit different symptoms compared to adults. These can include loud snoring, pauses in breathing during sleep, restless sleep, mouth breathing, excessive sweating during sleep, bedwetting, difficulty waking up in the morning, and daytime sleepiness. Behavioral issues, poor school performance, and growth problems may also be observed.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis of sleep apnea in children often involves a comprehensive evaluation, including a review of symptoms, physical examination, and a sleep study. The sleep study assesses breathing patterns, oxygen levels, brain activity, and other parameters during sleep.
-
Treatment options: Treatment for sleep apnea in children may depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Removal of tonsils and adenoids (adenotonsillectomy) is a common treatment option when enlarged tonsils or adenoids are the primary cause. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy or other non-surgical interventions may be considered in certain cases.
-
Long-term effects: Sleep apnea in children, if left untreated, can lead to various complications, including growth issues, developmental delays, behavioral problems, and poor academic performance. It is important to address sleep apnea in children to promote healthy growth, development, and overall well-being.
If you suspect that your child may have sleep apnea, it is crucial to consult a pediatrician or a sleep specialist for proper evaluation and treatment.
Understanding the symptoms and characteristics of sleep apnea in adults and children can help individuals seek timely medical attention and access appropriate treatment options.
SA (Sleep Apnea) Treatments:
SA (Sleep Apnea) can be effectively managed through various treatment approaches tailored to individual needs. Here are some common treatments for SA:
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve SA symptoms. These may include weight loss, regular exercise, avoiding alcohol and sedatives, and sleeping on your side instead of your back. These modifications can help reduce the severity of SA and promote better sleep.
-
CPAP Therapy (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure): CPAP therapy is considered the gold standard treatment for SA. It involves using a CPAP machine that delivers a continuous stream of pressurized air through a mask worn over the nose or mouth during sleep. The gentle air pressure helps keep the airway open, preventing apneas and improving breathing. CPAP therapy effectively reduces snoring, improves sleep quality, and alleviates daytime sleepiness.
-
Oral Appliances: Oral appliances are custom-made devices that are worn during sleep. They are designed to reposition the jaw and tongue, helping to keep the airway open and reducing SA episodes. Oral appliances are particularly useful for individuals with mild to moderate SA or those who cannot tolerate CPAP therapy. They are comfortable to wear and can improve sleep quality by reducing snoring and enhancing airflow.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist to determine the most suitable treatment option for your SA. They will consider the severity of your SA, your overall health, and your personal preferences to develop a treatment plan that best suits your needs. Adhering to the prescribed treatment consistently is key to effectively managing SA and improving your quality of life.
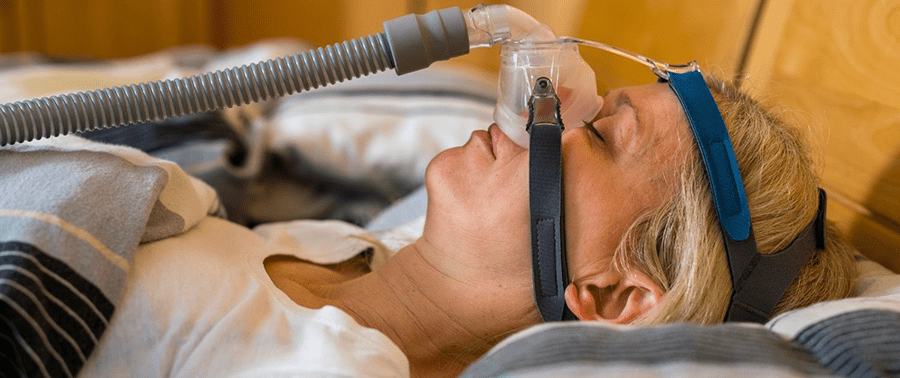
CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) Therapy
CPAP therapy (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) is a highly effective treatment for SA. It involves using a CPAP machine to deliver a continuous flow of pressurized air to the airway during sleep. Here’s how CPAP therapy works and its benefits:

-
How CPAP Works: A CPAP machine consists of a motor, a mask, and a hose. The motor generates pressurized air, which is delivered through the hose and mask worn over the nose, mouth, or both. The continuous flow of air acts as a splint, keeping the airway open and preventing it from collapsing or becoming obstructed during sleep.
-
Benefits of CPAP Therapy: CPAP therapy offers numerous benefits for individuals with SA. It effectively eliminates or significantly reduces apneas and hypopneas, promoting uninterrupted breathing throughout the night. By improving airflow, CPAP therapy reduces snoring and restores normal oxygen levels, leading to better sleep quality. CPAP therapy also alleviates daytime symptoms such as excessive daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and cognitive impairments, allowing individuals to feel more alert and refreshed during the day.
-
Types of CPAP Machines: There are various types of CPAP machines available, including standard CPAP machines, Auto-CPAP machines (APAP), and Bi-level positive airway pressure (BiPAP) machines. The type of machine recommended will depend on the individual’s specific needs and the guidance of their healthcare provider.
-
Mask Options: CPAP masks come in different styles and sizes to accommodate individual preferences and facial structures. Common mask types include nasal masks, full-face masks, and nasal pillow masks. It is important to find a mask that provides a secure and comfortable fit to ensure optimal therapy effectiveness.
CPAP therapy is a highly effective and widely used treatment option for SA. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist to receive proper CPAP machine setup, mask fitting, and ongoing support to ensure successful treatment outcomes.
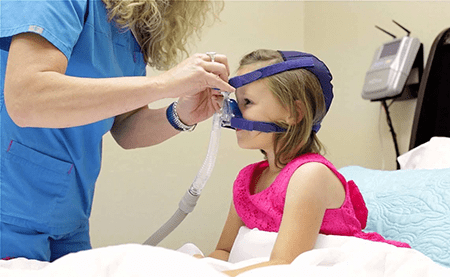
Oral Appliances for SA
Oral appliances are an alternative treatment option for SA, particularly for individuals with mild to moderate SA or those who cannot tolerate CPAP therapy. Here’s what you need to know about oral appliances:
-
How Oral Appliances Work: Oral appliances are custom-made devices that are worn in the mouth during sleep. They are designed to reposition the jaw, tongue, and soft tissues to keep the airway open and reduce SA episodes. By advancing the lower jaw or holding the tongue in a forward position, oral appliances help prevent airway collapse and promote improved airflow.
-
Benefits of Oral Appliances: Oral appliances offer several benefits for SA treatment. They are comfortable, non-invasive, and easy to use. Unlike CPAP therapy, oral appliances do not require a machine or mask, making them more convenient for travel. Oral appliances also have a high compliance rate due to their ease of use and comfort, increasing the likelihood of consistent usage and treatment success.
-
Types of Oral Appliances: There are different types of oral appliances available for SA treatment. The two most common types are mandibular advancement devices (MADs) and tongue-retaining devices (TRDs). MADs reposition the lower jaw, while TRDs hold the tongue in a forward position. The specific type of oral appliance recommended will depend on individual factors and the guidance of a dentist or sleep specialist.
-
Customization and Fitting: Oral appliances are custom-made to fit the individual’s mouth and teeth. The process involves dental impressions, which are used to create a personalized appliance that provides a comfortable and secure fit. Regular follow-up visits with the dentist are necessary to monitor the effectiveness of the appliance and make any necessary adjustments.
It is important to consult with a dentist or sleep specialist experienced in oral appliance therapy to determine if it is a suitable treatment option for your SA. They will assess your specific needs, evaluate your oral health, and provide personalized recommendations to help you manage your SA effectively.
SA Management
Effective management of SA (Sleep Apnea) involves a comprehensive approach that addresses various aspects of the condition. Here are some key areas of SA management:
-
Medical Treatment: Seeking medical treatment is crucial for managing SA. This may involve using treatments such as CPAP therapy, oral appliances, positional therapy, or surgery, depending on the severity and underlying causes of SA. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for your SA.
-
Weight Management: Weight management plays a significant role in managing SA, particularly in cases where excess weight is a contributing factor. Losing weight can help reduce the severity of SA and improve symptoms. Adopting a healthy and balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and seeking guidance from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can support effective weight management.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Making certain lifestyle changes can have a positive impact on SA management. These include avoiding alcohol and sedatives, which can relax the airway muscles and contribute to breathing problems during sleep. Additionally, practicing good sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and establishing a relaxing bedtime routine, can promote better sleep quality.
-
Positional Therapy: Positional therapy focuses on adjusting sleeping positions to minimize airway obstruction during sleep. For individuals with positional SA, in which the airway becomes blocked in specific sleeping positions, positional therapy can be beneficial. Techniques such as using specialized pillows or wearing devices that prevent sleeping on the back (supine avoidance) can help maintain an open airway and reduce SA episodes.
-
Continuous Monitoring: Regular monitoring of SA is important to assess treatment effectiveness and make necessary adjustments. This may involve undergoing sleep studies, such as polysomnography, to evaluate the severity of SA and measure treatment outcomes. Healthcare professionals can use the data obtained from these studies to guide treatment decisions and optimize SA management.
-
Collaborative Care: SA management often involves a multidisciplinary approach, involving healthcare professionals from different specialties. This may include sleep specialists, pulmonologists, dentists, dietitians, and psychologists. Collaborative care ensures a comprehensive evaluation of the individual’s condition and provides tailored treatment plans that address all aspects of SA management.
Remember, SA management is a lifelong commitment, and ongoing adherence to treatment recommendations is essential for long-term success. By following a comprehensive management plan, individuals with SA can effectively control their symptoms, improve their quality of sleep, and enhance their overall well-being.
SA Devices
SA (Sleep Apnea) devices refer to the various types of equipment and products designed to help manage SA symptoms and improve sleep quality. Here are some commonly used SA devices:
-
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Machines: CPAP machines are the most widely used devices for SA treatment. They deliver a constant stream of pressurized air through a mask worn over the nose, mouth, or both during sleep. The pressurized air helps keep the airway open, preventing apneas and improving breathing. CPAP machines come in different models and features, allowing individuals to find a device that suits their needs and preferences.
-
Bi-level Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) Machines: BiPAP machines provide two levels of pressure: a higher pressure during inhalation and a lower pressure during exhalation. This feature can be beneficial for individuals who require more assistance during breathing, especially those with certain medical conditions or respiratory muscle weakness.
-
Automatic Positive Airway Pressure (APAP) Machines: APAP machines are designed to automatically adjust the pressure levels based on an individual’s breathing patterns throughout the night. These devices continuously monitor the airway and deliver the most appropriate pressure to maintain airway patency and optimize therapy effectiveness.
-
Oral Appliances: Oral appliances are custom-made devices worn in the mouth during sleep. They are designed to reposition the jaw, tongue, and soft tissues to keep the airway open and reduce SA episodes. Oral appliances are particularly useful for individuals with mild to moderate SA or those who cannot tolerate CPAP therapy. They are comfortable, portable, and offer an alternative treatment option for SA management.
-
Adaptive Servo-Ventilation (ASV) Devices: ASV devices are primarily used for treating complex or central SA, where the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. These devices monitor the individual’s breathing pattern and deliver varying pressures to ensure adequate ventilation and normalize breathing during sleep.
-
Positional Therapy Devices: Positional therapy devices are designed to help individuals maintain a specific sleeping position that minimizes airway obstruction. They include specialized pillows, vests, and positional alarms that alert individuals when they adopt a position that increases the likelihood of SA episodes. These devices can be effective for individuals with positional SA.
-
Nasal Dilators and Strips: Nasal dilators are small devices inserted into the nostrils to help keep the nasal passages open, promoting improved airflow. Nasal strips are adhesive strips placed on the outside of the nose, gently lifting and widening the nasal passages. These devices can be beneficial for individuals with nasal congestion or obstruction contributing to SA.
-
Sleep Apnea Monitors: Sleep apnea monitors are portable devices used for at-home sleep monitoring. They measure vital signs, oxygen levels, and breathing patterns during sleep to provide valuable information for diagnosis and treatment evaluation. Sleep apnea monitors are particularly useful for individuals who cannot undergo traditional in-lab sleep studies.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist to determine the most suitable SA device for your specific needs. They will consider factors such as the severity of your SA, underlying health conditions, and personal preferences to guide you in selecting the appropriate device for effective SA management.
SA Products
SA (Sleep Apnea) products encompass a range of items that can support individuals with SA in their daily lives. These products aim to enhance comfort, convenience, and adherence to SA treatment. Here are some common SA products:
-
CPAP Masks: CPAP masks come in various styles and sizes to cater to individual preferences and facial structures. They include nasal masks, full-face masks, nasal pillow masks, and hybrid masks. Choosing a well-fitting mask that provides a comfortable seal is essential for effective CPAP therapy.
-
CPAP Accessories: CPAP accessories include items that complement CPAP therapy, such as hose management systems, mask liners, mask wipes, filters, and tubing wraps. These products can enhance comfort, hygiene, and overall CPAP experience.
-
Travel-friendly SA Products: Travel-friendly SA products are designed for individuals who need to continue their SA treatment while on the go. These may include compact CPAP machines, portable battery packs, travel-sized mask cleaners, and lightweight travel bags. These products make it easier for individuals to maintain their SA therapy during travel or when away from home.
-
SA Pillows: SA pillows are specially designed to provide optimal support for individuals with SA. They feature contoured shapes and strategic padding to help align the head, neck, and spine, reducing the risk of airway obstruction during sleep. SA pillows can enhance comfort and promote better sleep quality.
-
CPAP Humidifiers: CPAP humidifiers add moisture to the air delivered by CPAP machines, preventing dryness and irritation of the airways and nasal passages. Humidifiers can alleviate common CPAP side effects, such as dry throat, nasal congestion, and discomfort.
-
Snoring and SA Apps: Snoring and SA apps are smartphone applications that utilize sound analysis algorithms to detect and record snoring and SA episodes during sleep. These apps can provide individuals with valuable insights into their sleep patterns and help monitor the effectiveness of SA treatment.
-
Educational Resources: Educational resources in the form of books, pamphlets, websites, and online forums provide information, guidance, and support for individuals with SA. These resources cover various topics related to SA, including treatment options, lifestyle recommendations, and coping strategies.
Remember to consult with healthcare professionals or sleep specialists before purchasing SA devices or products. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific needs and ensure that the chosen products are compatible with your SA treatment plan.
SA Solutions
Managing SA (Sleep Apnea) requires adopting various solutions to address the underlying causes and symptoms of the condition. Here are some effective SA solutions:
-
Weight Management: Obesity and excess weight are significant risk factors for SA. Losing weight through a combination of a healthy diet and regular exercise can help reduce the severity of SA and improve overall sleep quality. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a tailored weight management plan.
-
Positional Therapy: Positional therapy focuses on adjusting sleeping positions to minimize airway obstruction during sleep. For individuals with positional SA, changing sleeping positions can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of SA episodes. Techniques such as using specialized pillows or wearing devices that prevent sleeping on the back (supine avoidance) can be effective SA solutions.
-
Behavioral Changes: Certain lifestyle modifications can contribute to SA management. Avoiding alcohol, sedatives, and smoking can help minimize airway muscle relaxation and respiratory disturbances during sleep. Practicing good sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a comfortable sleep environment, can also promote better sleep quality and reduce SA symptoms.
-
Oral Appliances: Oral appliances are custom-made devices that can be used as an alternative to CPAP therapy for managing SA. They work by repositioning the jaw, tongue, and soft tissues to maintain an open airway during sleep. Oral appliances are particularly beneficial for individuals with mild to moderate SA or those who cannot tolerate CPAP therapy.
-
Surgical Interventions: In some cases, surgical interventions may be considered as SA solutions. Surgical procedures aim to correct structural abnormalities in the airway, such as removing excess tissue, correcting nasal deformities, or repositioning the jaw. Surgery is typically recommended for individuals with severe SA who have not responded to other treatment options.
-
Positive Airway Pressure Therapy: Positive airway pressure therapy, such as CPAP or BiPAP therapy, is the most common and effective treatment for SA. These therapies deliver pressurized air to keep the airway open during sleep, preventing apneas and improving breathing. Compliance with positive airway pressure therapy is crucial for achieving optimal SA management.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist to determine the most appropriate SA solutions for your specific needs. They will assess your SA severity, medical history, and individual preferences to create a comprehensive SA management plan that may include a combination of lifestyle modifications, devices, and other interventions.
SA Clinic
An SA (Sleep Apnea) clinic is a specialized medical facility dedicated to the diagnosis, treatment, and management of SA. SA clinics are staffed by healthcare professionals who specialize in sleep medicine, such as sleep physicians, pulmonologists, and respiratory therapists. These clinics provide comprehensive care for individuals with SA and offer a range of services, including:
-
Sleep Studies: SA clinics typically offer in-lab sleep studies or home sleep testing (HST) to diagnose SA. Sleep studies involve monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep, such as brain waves, heart rate, oxygen levels, and respiratory patterns. These studies help assess the presence and severity of SA, guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
-
Consultations and Evaluations: SA clinics provide consultations and evaluations with sleep specialists who assess individual cases, review medical histories, and perform physical examinations. These consultations help determine the most suitable treatment options and develop personalized SA management plans.
-
Treatment Planning and Follow-up: SA clinics work closely with patients to develop tailored treatment plans based on their specific needs. This includes prescribing appropriate therapies, such as PAP or OAT, and providing guidance on lifestyle modifications. SA clinics also offer regular follow-up appointments to monitor treatment progress, adjust therapies if necessary, and address any concerns or issues.
-
Patient Education and Support: SA clinics play a vital role in educating patients about SA, its management, and the importance of treatment adherence. They provide resources, educational materials, and support to help individuals understand their condition better and actively participate in their SA treatment.
-
Collaboration with Other Specialists: SA clinics often collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as dentists, ENT specialists, and weight management experts, to ensure comprehensive care for individuals with SA. This multidisciplinary approach addresses all aspects of SA management and promotes optimal treatment outcomes.
If you suspect you have SA or have been diagnosed with SA, consulting an SA clinic is recommended. They have the expertise and resources to provide accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing support to improve your sleep quality and overall well-being.
SA Specialist
An SA (Sleep Apnea) specialist is a healthcare professional who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of SA. These specialists have in-depth knowledge and expertise in sleep medicine, specifically related to SA. Some common types of SA specialists include:
-
Sleep Physicians: Sleep physicians are medical doctors who specialize in sleep medicine. They are trained in diagnosing and treating various sleep disorders, including SA. Sleep physicians often work in sleep clinics or sleep centers and play a key role in evaluating patients, conducting sleep studies, prescribing appropriate treatments, and providing long-term care for individuals with SA.
-
Pulmonologists: Pulmonologists are medical doctors who specialize in diseases and disorders of the respiratory system, including SA. They have expertise in diagnosing and managing respiratory conditions that may contribute to SA, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or asthma. Pulmonologists may collaborate with sleep physicians to develop comprehensive treatment plans for individuals with SA.
-
Dentists: Dentists who specialize in dental sleep medicine can also be SA specialists. These dentists have additional training and certification in treating SA using oral appliances. They work closely with patients to design, fit, and adjust custom oral devices that help maintain an open airway during sleep. Dentists who specialize in SA provide valuable non-invasive treatment options for individuals with mild to moderate SA or those who cannot tolerate PAP therapy.
-
ENT Specialists: Ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialists, also known as otolaryngologists, are physicians who specialize in disorders of the head and neck, including those affecting the airway. ENT specialists evaluate and manage anatomical abnormalities in the nose, throat, and upper airway that may contribute to SA. They may recommend surgical interventions or collaborate with other SA specialists to develop comprehensive treatment plans.
SA specialists work together to provide integrated care for individuals with SA, ensuring accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing management. Consultation with an SA specialist is recommended for individuals experiencing symptoms of SA or seeking expert guidance in SA diagnosis and treatment.
Related Links
Conclusion:Â
In conclusion, SA (Sleep Apnea) is a common sleep disorder characterized by repetitive pauses in breathing during sleep, leading to disrupted sleep patterns and potential health complications. It is essential to raise awareness about SA and promote early detection and appropriate treatment for this condition.
Throughout this article, we have explored various aspects of SA, including its definition, types, symptoms, causes, and treatment options. SA can affect individuals of all ages, from children to adults, and can have a significant impact on overall well-being and quality of life.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of SA is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include loud snoring, excessive daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, and frequent awakenings during the night. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect SA or experience these symptoms to undergo a proper evaluation.
Diagnosing SA often involves sleep studies, which monitor physiological parameters during sleep to assess the presence and severity of the condition. Once diagnosed, various treatment options are available to manage SA effectively and improve sleep quality.
Positive Airway Pressure Therapy (PAP), such as CPAP or BiPAP therapy, is considered the gold standard treatment for SA. These therapies deliver pressurized air to keep the airway open during sleep, preventing apneas and improving breathing. Oral appliance therapy, lifestyle modifications, positional therapy, and surgical interventions are other treatment modalities that may be considered based on the individual’s specific needs and preferences.
Effective SA management requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving collaboration between sleep specialists, dentists, pulmonologists, and other healthcare professionals. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, such as weight management and adopting healthy sleep habits, can significantly contribute to the overall management of SA.
By addressing SA and promoting better sleep, individuals can enhance their overall health and well-being. Improved sleep quality not only reduces the risks associated with SA but also enhances daytime alertness, cognitive function, and overall quality of life.
In conclusion, early recognition, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are key in managing SA effectively. If you suspect you or a loved one may have SA, it is crucial to seek medical attention and explore the available treatment options. Remember, better sleep leads to a better life.
Q: 1. What is SA (Sleep Apnea)?
A: SA, also known as Sleep Apnea, is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep. These interruptions in breathing can occur multiple times throughout the night and disrupt normal sleep patterns.
Q: 2. What are the common symptoms of SA?
A: Common symptoms of SA include loud snoring, excessive daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, gasping or choking during sleep, difficulty concentrating, and restless sleep. It’s important to note that not everyone with SA experiences the same symptoms.
Q: 3. Who is at risk for SA?
A: SA can affect individuals of any age and gender. However, certain factors increase the risk, including being overweight or obese, having a family history of SA, being over the age of 40, having a thick neck circumference, and having certain anatomical features like a deviated septum.
Q: 4. How is SA diagnosed?
A: SA is typically diagnosed through a sleep study called polysomnography. This study measures various physiological parameters during sleep, such as brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, breathing patterns, and oxygen levels, to assess the presence and severity of SA.
Q: 5. What are the treatment options for SA?
A: Treatment options for SA include Positive Airway Pressure Therapy (PAP) using devices like CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) or BiPAP (Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure), which deliver pressurized air to keep the airway open during sleep. Oral appliances, lifestyle modifications, positional therapy, and, in some cases, surgery may also be recommended.
Q: 6. Can lifestyle changes help with SA management?
A: Yes, adopting certain lifestyle modifications can contribute to the management of SA. These may include maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime, establishing a consistent sleep schedule, and sleeping in a position that promotes optimal breathing.
More Links
Treatments of Sleep Apnea in Children |
Sleep Apnea |