Psoriasis: Discovering Practical Solutions for an Unforgettable Triumph Over Skin Challenges – Top 5 Tips for Managing and Overcoming

What are 3 symptoms of psoriasis? :
Psoriasis presents with a range of symptoms, but three key symptoms can help identify the condition.
Firstly, itchy skin is a common symptom, causing discomfort and irritation. The intense itching is often accompanied by redness and inflammation in the affected areas. Scratching the itchy patches can worsen the condition and even lead to the development of open sores or lesions. Managing the itchiness associated with psoriasis often involves a combination of topical treatments, moisturizers, and lifestyle modifications.
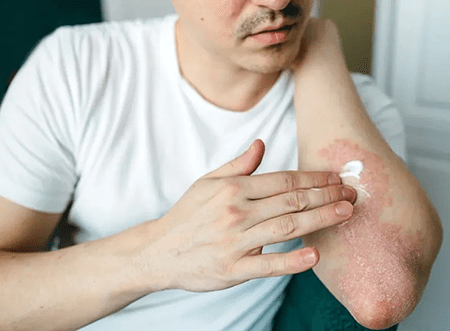
Secondly, red patches characterize psoriasis, with the affected areas exhibiting raised, inflamed skin. The redness is caused by increased blood flow to the affected skin due to the underlying inflammation. These patches can vary in size and severity and may be accompanied by a silvery-white scale. Managing red patches involves a comprehensive approach, including the use of topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic medications, and lifestyle modifications.
Lastly, thickened nails are a distinct symptom of psoriasis. Psoriasis can affect the nails, leading to changes such as thickening, pitting, ridges, discoloration, or even nail detachment. Proper nail care and treatment can help manage psoriatic nail dystrophy and minimize its impact on daily life.
Recognizing these three symptoms—itchy skin, red patches, and thickened nails—can aid in early identification and prompt treatment of psoriasis. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management strategies.
Itchy Skin and Psoriasis
Itchy skin is a common symptom experienced by individuals with psoriasis. The intense itchiness can be attributed to the inflammation and rapid skin cell turnover associated with the condition.
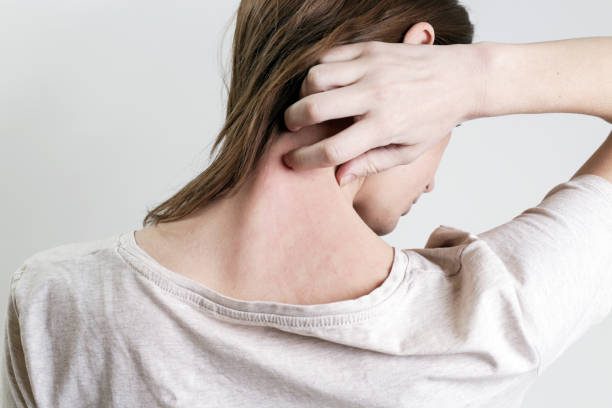

Psoriasis accelerates the production of new skin cells, causing them to build up rapidly on the skin’s surface. These thickened patches of skin become itchy and can lead to a persistent urge to scratch.
However, scratching the affected areas can worsen the condition and even result in the development of open sores or lesions. To alleviate the itchiness, various treatments such as topical creams, moisturizers, and prescribed medications can be used.
Additionally, keeping the skin well-moisturized and avoiding triggers that worsen the itching can help manage this distressing symptom.
Red Patches and Psoriasis
Red patches are one of the most recognizable symptoms of psoriasis. These patches typically appear as raised, inflamed areas on the skin and can vary in size and severity.
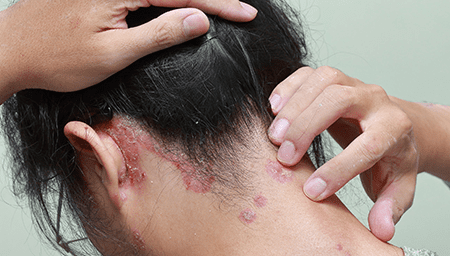
The redness is caused by increased blood flow to the affected skin due to the underlying inflammation. In some cases, the red patches may be accompanied by a silvery-white scale that covers the surface.
These scales are a result of the excessive growth and shedding of skin cells associated with psoriasis. The most commonly affected areas include the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back, although psoriasis can occur on any part of the body.
Managing red patches involves a comprehensive approach, including the use of topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic medications, and lifestyle modifications such as stress reduction and maintaining a healthy diet.
Thickened Nails and Psoriasis
Psoriasis can also affect the nails, leading to changes known as psoriatic nail dystrophy. Thickened nails are a distinct symptom associated with this condition.
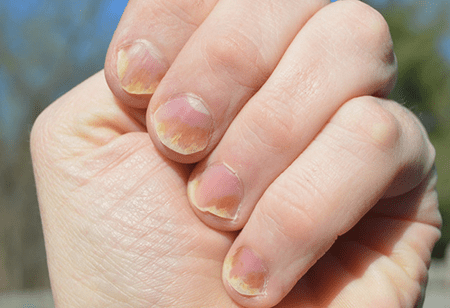
Individuals with psoriasis may notice their nails becoming thicker and harder than usual. Additionally, the nails may develop irregularities such as pitting, ridges, or discoloration.
In more severe cases, the nails may even crumble or detach from the nail bed. These nail changes can not only cause physical discomfort but also impact a person’s self-esteem.
Managing thickened nails involves a combination of approaches, including keeping the nails trimmed and clean, using specialized nail treatments, and seeking medical advice for severe cases.
By addressing the underlying psoriasis and adopting proper nail care practices, individuals can minimize the impact of thickened nails on their daily lives.
What is the most serious type of psoriasis? :
Among the different types of psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis is considered the most serious and severe. It is a rare form of psoriasis that affects the entire body. Erythrodermic psoriasis is characterized by widespread redness, inflammation, and shedding of the skin. The skin may appear as though it has been burned, and individuals with this type of psoriasis often experience intense itching, pain, and discomfort.

Erythrodermic psoriasis can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. The condition can disrupt the body’s ability to regulate temperature, leading to complications such as fluid and electrolyte imbalances. In addition, the compromised skin barrier can increase the risk of infection.
The exact cause of erythrodermic psoriasis is not fully understood, but it can occur as a result of poorly managed plaque psoriasis, abrupt withdrawal of systemic medications, or severe sunburn. It is essential for individuals with erythrodermic psoriasis to seek medical care from a dermatologist or healthcare professional experienced in managing severe psoriasis.
Treatment for erythrodermic psoriasis involves a combination of approaches aimed at stabilizing the condition, relieving symptoms, and preventing complications. This may include hospitalization, topical medications, systemic therapies, supportive care, and close monitoring by healthcare professionals.
In summary, while psoriasis encompasses various types with distinct characteristics, plaque psoriasis remains the most common form. Guttate psoriasis presents with small, widespread spots, and inverse psoriasis affects skin folds. However, the most serious type of psoriasis is erythrodermic psoriasis, which requires immediate medical attention due to its widespread inflammation and potential life-threatening complications. It is crucial for individuals with psoriasis to work closely with healthcare professionals to manage their condition effectively and improve their quality of life.
Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is the most common type of psoriasis, accounting for approximately 80% of all cases. It is characterized by the development of thick, raised, and inflamed patches of skin called plaques. These plaques are typically covered with silvery-white scales and can appear on various parts of the body, including the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
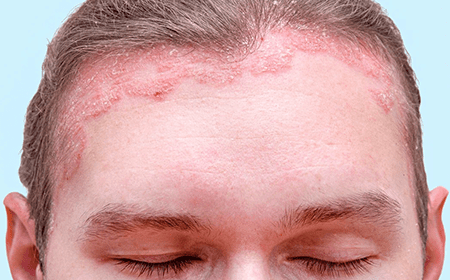
Plaque psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This leads to an overproduction of skin cells, causing them to accumulate rapidly on the skin’s surface. As a result, the plaques form, causing itching, discomfort, and sometimes pain.
While the exact cause of plaque psoriasis is unknown, it is believed to be influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Triggers such as stress, infections, certain medications, and changes in weather conditions can exacerbate the condition.
Treatment for plaque psoriasis aims to reduce inflammation, slow down the rapid skin cell turnover, and relieve symptoms. Options include topical treatments, such as corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, phototherapy, systemic medications, and lifestyle modifications. It’s important for individuals with plaque psoriasis to work closely with healthcare professionals to find the most effective treatment plan for their specific needs.
Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis is a distinct form of psoriasis characterized by the appearance of small, red, and scaly spots on the skin. These spots are usually smaller and more widespread than the plaques seen in plaque psoriasis. Guttate psoriasis often occurs suddenly and is commonly triggered by bacterial or viral infections, particularly streptococcal throat infection.
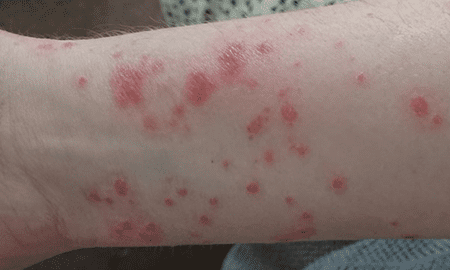
This type of psoriasis is more common in children, teenagers, and young adults. The exact cause of guttate psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors.
The spots in guttate psoriasis typically appear on the trunk, limbs, and scalp. They may be accompanied by itching and can sometimes develop into larger plaques over time. Guttate psoriasis often resolves on its own within a few weeks or months, but in some cases, it may persist or recur.
Treatment for guttate psoriasis aims to alleviate symptoms and prevent further flare-ups. Topical corticosteroids, moisturizers, and coal tar preparations are commonly used to reduce inflammation and itching. In cases where streptococcal infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed. Phototherapy and systemic medications are reserved for more severe or persistent cases.
Inverse Psoriasis
Inverse psoriasis, also known as flexural psoriasis, is characterized by smooth, red, and inflamed patches of skin that appear in skin folds. Unlike plaque psoriasis, inverse psoriasis does not typically have the thick, scaly plaques. It commonly affects areas such as the armpits, groin, under the breasts, and in the folds of the buttocks.
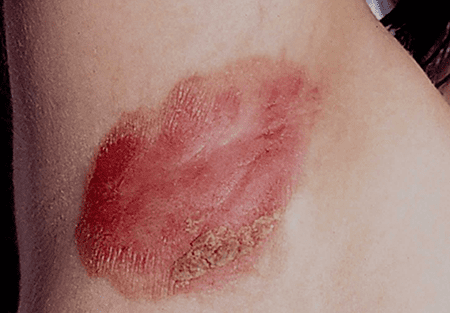
The exact cause of inverse psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to be linked to genetic factors, as well as friction and moisture in the affected areas. Heat and sweating can exacerbate the condition, making it particularly uncomfortable for individuals.
The symptoms of inverse psoriasis may include redness, itching, and sensitivity. The skin folds affected by inverse psoriasis can become prone to secondary infections due to the warm and moist environment.
Treatment for inverse psoriasis focuses on reducing inflammation, relieving symptoms, and managing moisture in the affected areas. Topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and anti-yeast medications may be prescribed to alleviatethe symptoms and control the inflammation. It is also important to keep the affected areas clean and dry, as well as avoid irritants or triggers that may worsen the condition. In some cases, systemic medications or phototherapy may be recommended for more severe or persistent cases of inverse psoriasis.
What is main cause of psoriasis ( psoriatic dermatitis )? :
The main cause of psoriatic dermatitis, also known as psoriasis, is a combination of genetic predisposition and immune system dysfunction. In individuals with a genetic predisposition to the condition, certain genes related to immune system regulation and skin cell turnover can contribute to their susceptibility to psoriasis.
When these individuals encounter certain environmental triggers, such as stress, infections, injury to the skin, or specific medications, their immune system becomes dysregulated. This dysregulation causes an abnormal inflammatory response, leading to the rapid production of skin cells and the characteristic plaques and red, inflamed patches seen in psoriatic dermatitis.
While the exact triggers and mechanisms may vary among individuals, the interplay between genetics, immune system dysfunction, and environmental factors is considered the primary cause of psoriatic dermatitis. Understanding these underlying factors is crucial for developing effective treatments and management strategies for individuals with psoriatic dermatitis. By addressing both genetic predisposition and environmental triggers, healthcare professionals can tailor personalized treatment plans to improve the quality of life for those affected by this chronic skin condition.
Genetic Predisposition
Psoriatic dermatitis, like many other medical conditions, can have a genetic component. Individuals with a family history of psoriasis are more likely to develop the condition themselves. Certain genes play a role in regulating the immune system and skin cell turnover, and variations in these genes can increase the risk of psoriatic dermatitis.
Having a genetic predisposition to psoriatic dermatitis does not guarantee that a person will develop the condition, but it does increase the likelihood. Understanding the genetic factors involved in psoriasis is essential for better diagnosis, treatment, and management of the condition. If someone has a family history of psoriasis, it is important for them to be aware of the increased risk and monitor their skin for any signs of psoriatic dermatitis.
Immune System Dysfunction
The immune system plays a crucial role in protecting the body from infections and other threats. In the case of psoriatic dermatitis, the immune system becomes dysregulated, leading to an abnormal response that affects the skin. In individuals with psoriatic dermatitis, the immune system mistakenly identifies healthy skin cells as foreign invaders, triggering an inflammatory response.
This immune system dysfunction causes an overproduction of skin cells, leading to their rapid accumulation on the skin’s surface. The result is the characteristic thick, raised plaques and red, inflamed skin patches seen in psoriatic dermatitis.
The exact mechanisms that cause immune system dysfunction in psoriatic dermatitis are still being studied. However, research has shown that certain immune cells, such as T cells and cytokines, play a significant role in the inflammatory process. Understanding the immune system’s involvement in psoriasis is crucial for developing targeted treatments that can effectively manage the condition.
Environmental Triggers
While genetics and immune system dysfunction are major factors in psoriatic dermatitis, environmental triggers can also play a role in exacerbating the condition. Various environmental factors can lead to flare-ups or worsening of psoriatic dermatitis symptoms in susceptible individuals.
Common environmental triggers include stress, infections (such as streptococcal throat infections), injury or trauma to the skin, certain medications, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption. Cold and dry weather can also trigger or worsen psoriatic dermatitis in some individuals.
Identifying and avoiding these triggers can be instrumental in managing psoriatic dermatitis and reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Healthcare professionals often work with individuals to develop personalized management plans that consider both genetic factors and environmental triggers to effectively control the condition.
Can psoriasis be prevented? :
Psoriatic dermatitis, like other chronic conditions, cannot be entirely prevented. However, certain measures can be taken to reduce the risk of developing psoriatic dermatitis or to minimize its severity.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall skin health and reduce the likelihood of developing psoriatic dermatitis. This includes following a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption.
Managing stress is another key aspect of prevention. High levels of stress have been linked to an increased risk of developing psoriatic dermatitis and triggering flare-ups in individuals already affected by the condition. Incorporating stress reduction techniques into daily life, such as relaxation exercises, engaging in enjoyable activities, and seeking support, can help mitigate the impact of stress on the body.
It’s important to note that while lifestyle modifications can be beneficial, they may not guarantee prevention or complete control of psoriatic dermatitis. The condition has a multifactorial nature, involving genetic predisposition and immune system dysfunction. Individuals with a family history of psoriatic dermatitis should remain vigilant and seek early diagnosis and treatment if symptoms arise. Consulting with a healthcare professional or dermatologist can provide personalized guidance and recommendations for managing psoriatic dermatitis effectively.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting certain lifestyle modifications can have a positive impact on managing psoriatic dermatitis. While lifestyle changes cannot cure the condition, they can help reduce symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and improve overall well-being.
Maintaining a healthy weight is important as excess weight can worsen psoriatic dermatitis. Regular exercise, such as aerobic activities and strength training, can help control weight and reduce inflammation. However, individuals with psoriatic dermatitis should choose low-impact exercises that minimize joint stress and friction on affected areas.
Dietary modifications may also be beneficial. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can support overall skin health and reduce inflammation. Some individuals find that eliminating certain trigger foods, such as gluten or dairy, can help manage their symptoms. It’s important to work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the most suitable dietary approach for managing psoriatic dermatitis.
Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption is essential, as these habits can worsen symptoms and trigger flare-ups. Both smoking and alcohol can weaken the immune system and increase inflammation in the body.
Stress Reduction
Stress is known to be a trigger for psoriatic dermatitis flare-ups. High levels of stress can worsen symptoms and contribute to inflammation in the body. Therefore, incorporating stress reduction techniques into daily life can be beneficial for individuals with psoriatic dermatitis.
Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or tai chi can help reduce stress levels. Engaging in enjoyable activities, such as hobbies, spending time with loved ones, or engaging in creative outlets, can also promote relaxation and provide a sense of well-being.
Regular physical exercise is not only beneficial for maintaining a healthy weight but also helps reduce stress levels. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood elevators that can improve overall mental well-being.
Additionally, seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can provide emotional support and a sense of community. Talking to a mental health professional or therapist can also be helpful in developing coping strategies to manage stress effectively.
What foods stop psoriasis?:
While there is no definitive list of foods that can stop psoriatic dermatitis, certain dietary strategies may help alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation.
Including foods that are rich in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and brightly colored fruits and vegetables, can have positive effects on skin health. These foods contain vitamins A, C, and E, as well as other phytochemicals that can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the body.
Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties. Omega-3s can help modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation in the body.
Adding turmeric, ginger, and garlic to meals can provide additional anti-inflammatory benefits. These spices contain compounds that have been shown tohave anti-inflammatory effects and may help reduce symptoms associated with psoriatic dermatitis.
It’s important to note that while certain foods may have potential benefits, dietary changes alone may not be sufficient to completely stop psoriatic dermatitis. The condition is multifactorial, involving genetic predisposition and immune system dysfunction. It is advisable to work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that combines appropriate medications, lifestyle modifications, and dietary strategies tailored to the individual’s specific needs.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet can be beneficial for individuals with psoriatic dermatitis. An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on consuming foods that help reduce inflammation in the body, which is a key factor in psoriatic dermatitis.
This diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds. It includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, nuts, and seeds. These foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals that can support overall skin health and help alleviate symptoms.
Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, can have anti-inflammatory effects on the body. Avoiding processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats is also recommended, as they can promote inflammation.
While an anti-inflammatory diet may not completely eliminate psoriatic dermatitis symptoms, it can help reduce inflammation, support the immune system, and improve overall well-being.
Gluten-Free Diet
For some individuals with psoriatic dermatitis, following a gluten-free diet may be beneficial. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, rye, and certain other grains. Some individuals with psoriatic dermatitis may have an underlying gluten sensitivity or celiac disease, which can trigger or worsen symptoms.
By eliminating gluten-containing foods from the diet, individuals can reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms associated with psoriatic dermatitis. Gluten-free alternatives include foods made from rice, corn, quinoa, and gluten-free oats.
It’s important to note that not all individuals with psoriatic dermatitis will benefit from a gluten-free diet. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making any significant dietary changes to determine if a gluten-free diet is appropriate for an individual’s specific condition.
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is often praised for its health benefits, including its potential positive impact on psoriatic dermatitis. This diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. It also includes moderate amounts of fish, poultry, and dairy products, while limiting red meat and processed foods.
The Mediterranean diet provides essential nutrients, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory compounds that can support skin health and reduce inflammation. The abundance of fruits and vegetables ensures a high intake of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which are essential for overall well-being.
The inclusion of healthy fats from sources like olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish provides omega-3 fatty acids and monounsaturated fats, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
While the Mediterranean diet is generally considered beneficial, it may not work the same way for everyone. It’s essential to work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to personalize dietary recommendations and ensure they align with individual needs and preferences.
What is the best treatment for psoriasis? :
Determining the best treatment for psoriatic dermatitis depends on various factors, including the severity of the condition, individual response to different treatments, and personal preferences.
Treatment options for psoriatic dermatitis range from topical medications to systemic therapies, phototherapy, and lifestyle modifications. Topical treatments, such as corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and calcineurin inhibitors, are commonly used for mild to moderate cases. They help reduce inflammation, soothe the skin, and control symptoms.
For more severe or resistant cases of psoriatic dermatitis, systemic therapies may be prescribed. These include oral medications, such as methotrexate or cyclosporine, or newer biologic therapies that target specific components of the immune system.
Phototherapy, which involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light, can also be an effective treatment option for psoriatic dermatitis. This can be done in a controlled medical setting or with the use of specialized home phototherapy devices.
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications such as stress reduction, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding triggers can contribute to managing psoriatic dermatitis.
The best treatment approach for psoriatic dermatitis is typically determined through a collaborative effort between the individual and their healthcare professional. It is important to consider the specific needs, preferences, and goals of the individual to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their unique situation. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential to evaluate treatment response and make necessary adjustments along the way.
Natural Remedies
Natural remedies are often sought by individuals with psoriatic dermatitis as complementary or alternative treatment options. While these remedies may not cure psoriatic dermatitis, they can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
One popular natural remedy is aloe vera, known for its soothing and moisturizing properties. Applying aloe vera gel or creams to affected areas may provide relief from itching and redness.
Another natural remedy is oatmeal baths. Adding colloidal oatmeal to warm bathwater and soaking in it can help soothe itchy and inflamed skin. Oatmeal has anti-inflammatory properties that can provide temporary relief.
Some individuals find relief by incorporating dietary supplements, such as fish oil or turmeric, into their regimen. Fish oil contains omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory effects, while turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with potential anti-inflammatory properties.
However, it is important to note that natural remedies may not work for everyone, and their effectiveness varies among individuals. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any natural remedies to ensure they are safe and appropriate for one’s specific condition.
Biologic Therapies
Biologic therapies are a newer class of medications that have revolutionized the treatment of psoriatic dermatitis. These medications target specific components of the immune system involved in the development of psoriatic dermatitis.
Biologics are usually administered through injections or infusions and work by blocking specific immune system proteins, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) or interleukins. By targeting these proteins, biologics help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms of psoriatic dermatitis.
Biologic therapies have shown great efficacy in managing moderate to severe psoriatic dermatitis that does not respond well to other treatment options. They have the potential to significantly improve skin clearance and quality of life for individuals with psoriatic dermatitis.
However, biologic therapies come with certain considerations, including the need for regular monitoring, potential side effects, and cost. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate biologic therapy and to monitor for any potential risks or adverse effects.
Related Links
|
Uncovering the Panic Causes of Bronchitis: A New Reasearch 2023 |
Innovative Study of Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A New Research 2023 |
Innovative Disease Melanoma: A New Complimentary Research 2023 |
Conclusion
In conclusion, psoriatic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition characterized by red, inflamed patches, and thick, raised plaques on the skin. While the exact cause of psoriatic dermatitis is not fully understood, it is believed to involve genetic predisposition, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers.
Managing psoriatic dermatitis requires a comprehensive approach that includes various treatment options and lifestyle modifications. Topical medications, systemic therapies, phototherapy, and biologic therapies are commonly used to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation. Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as stress reduction, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding triggers can play a significant role in managing the condition.
It is important for individuals with psoriatic dermatitis to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that suits their specific needs. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential to evaluate treatment response and make necessary adjustments. With proper management, individuals with psoriatic dermatitis can experience improved quality of life and better control over their symptoms.
Q: 1. Is psoriatic dermatitis contagious?
No, psoriatic dermatitis is not contagious. It is an autoimmune condition that is not spread through direct contact or airborne transmission.
Q: 2. Can psoriatic dermatitis be cured?
Psoriatic dermatitis is a chronic condition that currently has no cure. However, with proper treatment and management, it is possible to control symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve quality of life.
Q: 3. Are there any specific triggers for psoriatic dermatitis flare-ups?
Triggers for psoriatic dermatitis flare-ups can vary among individuals. Common triggers include stress, infections (such as streptococcal throat infections), injury to the skin, certain medications, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and changes in weather conditions.
Q: 4. Can diet affect psoriatic dermatitis?
Dietary changes, such as adopting an anti-inflammatory diet or eliminating gluten, may help alleviate symptoms for some individuals with psoriatic dermatitis. However, the impact of diet can vary among individuals, and it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes.
Q: 5. Can psoriatic dermatitis affect more than just the skin?
Yes, psoriatic dermatitis is not just a skin condition. It is associated with an increased risk of developing other health conditions, such as psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome. Regular monitoring and appropriate management are important to address potential comorbidities.
More Links

