Fibromyalgia: Discover the Mysteries, Empowering Solutions, and Top 5 Practical Insights

Overview
Fibromyalgia is a chronic and complex medical condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive difficulties. It is a condition that affects the way the brain processes pain signals, leading to increased sensitivity to pain and discomfort throughout the body. While the exact cause of fibromyalgia is still not fully understood, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. This condition predominantly affects women, and its symptoms can vary in intensity and duration, often leading to a significant impact on the quality of life for those affected. Management of fibromyalgia involves a multidisciplinary approach that may include medication, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and support from healthcare professionals.
5 Empowering Insights for Fibromyalgia
-
Holistic Treatment Approach: Adopting a holistic approach to managing fibromyalgia can be empowering. This involves combining traditional medical treatments with complementary therapies such as acupuncture, yoga, or meditation. Integrating these techniques into a personalized treatment plan can help improve pain management and overall well-being.
-
Exercise for Pain Relief: Engaging in regular low-impact exercises, such as swimming or walking, can have a positive impact on fibromyalgia symptoms. Exercise helps to release endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers, and can improve mood, sleep, and overall physical function.
-
Mind-Body Connection: Paying attention to the mind-body connection can be beneficial for fibromyalgia management. Practicing relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and stress reduction methods can help reduce anxiety, depression, and stress, which are often associated with fibromyalgia.
-
Supportive Community: Connecting with others who have fibromyalgia can provide a sense of empowerment and understanding. Joining support groups or online communities allows individuals to share experiences, coping strategies, and emotional support.
-
Self-Advocacy: Empowering oneself through self-advocacy involves actively participating in the management of the condition. Educating oneself about fibromyalgia, its symptoms, and available treatments can help individuals make informed decisions about their healthcare and lifestyle choices.
It’s important to remember that fibromyalgia affects each person differently, and what works for one individual may not work for another. Consulting with healthcare professionals and exploring various options can empower individuals with fibromyalgia to find a personalized and effective approach to managing their condition.
Intoduction :
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, predominantly women. It is characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive difficulties. This condition can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and daily functioning.
The exact cause of fibromyalgia is still unknown. However, research suggests that it may involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Some common risk factors for developing fibromyalgia include a family history of the condition, traumatic events, infections, and certain medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
The primary symptom of fibromyalgia is widespread pain that persists for at least three months. Individuals with fibromyalgia often experience tender points throughout their body, which are specific areas that are more sensitive to pressure. Alongside pain, other symptoms commonly associated with fibromyalgia include fatigue, sleep disturbances, cognitive difficulties (often referred to as “fibro fog”), headaches, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and mood disorders like depression and anxiety.
Diagnosing fibromyalgia can be challenging, as there are no specific laboratory tests or imaging studies that can definitively confirm the condition. Diagnosis is typically based on a combination of a thorough medical history, a physical examination, and the presence of specific tender points on the body. Doctors may also order blood tests to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
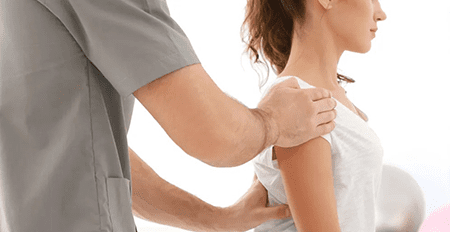
While there is no cure for fibromyalgia, various treatment approaches can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with the condition. The treatment plan is often personalized, considering the individual’s specific symptoms, preferences, and overall health. It typically involves a combination of medications, non-pharmacological treatments, and lifestyle modifications.
In conclusion, fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive difficulties. It can have a significant impact on an individual’s life. Although the exact cause is unknown, various treatment approaches can help manage the symptoms and improve overall well-being. In the following sections, we will explore the causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and lifestyle management techniques in more detail, providing a comprehensive understanding of fibromyalgia and how to cope with it effectively.
Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
The symptoms of fibromyalgia can vary from person to person, but the primary symptom is widespread pain that persists for at least three months. This pain often affects multiple areas of the body, including the muscles, joints, and soft tissues. Individuals with fibromyalgia may experience a constant dull ache or a more intense, throbbing pain.
Tender points are another characteristic feature of fibromyalgia. These are specific areas on the body that are more sensitive to pressure. Common tender points include the back of the head, shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees. Applying even mild pressure to these points can elicit pain or discomfort.
Fatigue

Fatigue is a common symptom experienced by individuals with fibromyalgia. It goes beyond normal tiredness and can be debilitating. People with fibromyalgia often wake up feeling unrefreshed, even after a full night’s sleep. The fatigue can be accompanied by a lack of energy, reduced stamina, and a feeling of constant exhaustion. This persistent fatigue can make it challenging to carry out daily activities and can significantly impact a person’s overall well-being.
Sleep Disturbances
Sleep disturbances are prevalent among individuals with fibromyalgia. Despite feeling exhausted, many people with fibromyalgia struggle to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night. They may wake up frequently, experience restless legs syndrome, or have other sleep disorders such as sleep apnea. The lack of restorative sleep further contributes to feelings of fatigue and can exacerbate other symptoms of fibromyalgia.
Cognitive Difficulties
Cognitive difficulties, often referred to as “fibro fog,” are common in fibromyalgia. Individuals may experience difficulties with memory, concentration, and attention span. They may have trouble finding the right words or feel mentally foggy. Fibro fog can significantly impact work, school, and daily tasks, making it challenging to focus and perform at one’s best.
Headaches
Headaches, including migraines, are frequently reported by individuals with fibromyalgia. These headaches can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as sensitivity to light and sound. The exact relationship between fibromyalgia and headaches is not fully understood, but they often coexist, contributing to the overall burden of the condition.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Many individuals with fibromyalgia also experience irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). IBS is a gastrointestinal disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. The precise connection between fibromyalgia and IBS is not yet clear, but research suggests that they may share similar underlying mechanisms, such as abnormalities in the way the brain and gut communicate.
Depression and Anxiety

Depression and anxiety are commonly associated with fibromyalgia. Living with chronic pain, fatigue, and other symptoms can take a toll on an individual’s mental well-being. The constant challenges and limitations imposed by fibromyalgia can lead to feelings of sadness, frustration, and hopelessness. Anxiety may arise from the unpredictability of symptoms and the impact they have on daily life. It is important for individuals with fibromyalgia to seek support and professional help to address these psychological aspects of the condition.
In the following sections, we will explore the causes, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment options, and lifestyle management techniques in more detail, providing a comprehensive understanding of fibromyalgia and how to cope with it effectively.
Causes of Fibromyalgia
The exact cause of fibromyalgia is still unknown, but research suggests that it may involve a combination of factors. Here are some potential causes that have been studied:
Central Sensitization
One of the key factors in fibromyalgia is central sensitization. It refers to an amplification of pain signals in the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. In individuals with fibromyalgia, the pain receptors in these areas become hypersensitive, leading to an increased perception of pain and a lowered pain threshold. This heightened sensitivity to pain can contribute to the widespread pain experienced by those with fibromyalgia.
Genetic Factors

There is evidence to suggest that genetic factors play a role in the development of fibromyalgia. Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of the condition are more likely to develop it themselves. While specific genes associated with fibromyalgia have not been identified, it is believed that genetic variations may influence the way the central nervous system processes pain signals and regulates pain sensitivity.
Neurochemical Imbalances
Research suggests that fibromyalgia may involve alterations in certain neurochemicals in the brain. These include serotonin, which regulates mood and pain perception, and substance P, which is involved in transmitting pain signals. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters may contribute to the heightened pain sensitivity and other symptoms experienced by individuals with fibromyalgia.
Physical or Emotional Trauma
Physical or emotional trauma, such as car accidents, injuries, or significant life stressors, have been linked to the development of fibromyalgia in some cases. Traumatic events can trigger changes in the central nervous system, leading to alterations in pain processing and sensitivity. The impact of trauma on the body and mind can contribute to the development or exacerbation of fibromyalgia symptoms.
Dysregulation of the Immune System
Emerging research suggests that dysregulation of the immune system may play a role in fibromyalgia. Abnormal immune responses and inflammation in the body could potentially contribute to the widespread pain and other symptoms experienced by individuals with fibromyalgia. However, the precise mechanisms and relationships between immune dysfunction and fibromyalgia are still being studied.
Chronic Stress and Hormonal Changes

Chronic stress and hormonal changes have been proposed as potential triggers or exacerbating factors for fibromyalgia. Prolonged stress can disrupt the body’s stress response system, leading to an imbalance in stress hormones such as cortisol. Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during menopause, may also influence pain perception and symptom severity in individuals with fibromyalgia.
It’s important to note that fibromyalgia is likely a complex condition with multiple contributing factors. These potential causes provide insights into the underlying mechanisms but do not fully explain the entire condition. Further research is needed to better understand the interplay between these factors and how they contribute to the development and progression of fibromyalgia.
Causes of Fibromyalgia ( Fibromyositis ):
The exact cause of fibromyositis is still unknown, but research suggests that it may involve a combination of factors. Here are some potential causes that have been studied:
Central Sensitization
One of the key factors in fibromyositis is central sensitization. It refers to an amplification of pain signals in the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. In individuals with fibromyositis, the pain receptors in these areas become hypersensitive, leading to an increased perception of pain and a lowered pain threshold. This heightened sensitivity to pain can contribute to the widespread pain experienced by those with fibromyositis.
Genetic Factors

There is evidence to suggest that genetic factors play a role in the development of fibromyositis. Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of the condition are more likely to develop it themselves. While specific genes associated with fibromyositis have not been identified, it is believed that genetic variations may influence the way the central nervous system processes pain signals and regulates pain sensitivity.
Neurochemical Imbalances
Research suggests that fibromyositis may involve alterations in certain neurochemicals in the brain. These include serotonin, which regulates mood and pain perception, and substance P, which is involved in transmitting pain signals. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters may contribute to the heightened pain sensitivity and other symptoms experienced by individuals with fibromyositis.
Physical or Emotional Trauma
Physical or emotional trauma, such as car accidents, injuries, or significant life stressors, have been linked to the development of fibromyositis in some cases. Traumatic events can trigger changes in the central nervous system, leading to alterations in pain processing and sensitivity. The impact of trauma on the body and mind can contribute to the development or exacerbation of symptoms in individuals with fibromyositis.
Dysregulation of the Immune System
Emerging research suggests that dysregulation of the immune system may play a role in fibromyositis. Abnormal immune responses and inflammation in the body could potentially contribute to the widespread pain and other symptoms experienced by individuals with fibromyositis. However, the precise mechanisms and relationships between immune dysfunction and fibromyositis are still being studied.
Chronic Stress and Hormonal Changes

Chronic stress and hormonal changes have been proposed as potential triggers or exacerbating factors for fibromyositis. Prolonged stress can disrupt the body’s stress response system, leading to an imbalance in stress hormones such as cortisol. Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during menopause, may also influence pain perception and symptom severity in individuals with fibromyositis.
It’s important to note that fibromyositis is likely a complex condition with multiple contributing factors. These potential causes provide insights into the underlying mechanisms but do not fully explain the entire condition. Further research is needed to better understand the interplay between these factors and how they contribute to the development and progression of fibromyositis.
Fibromyalgia (Fibromyositis) Prevention Strategies
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial for overall well-being and may contribute to reducing the risk or severity of fibromyositis symptoms. This includes engaging in regular physical activity, consuming a balanced diet, and getting enough restful sleep. Regular exercise, such as low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or yoga, can help improve muscle strength, reduce pain, and enhance overall physical and mental well-being. Eating a nutritious diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and provide the body with essential nutrients.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can exacerbate symptoms in individuals with fibromyositis. Finding effective stress management techniques can help reduce the impact of stress on the body and potentially minimize symptom flare-ups. This can include engaging in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or mindfulness practices. Additionally, incorporating activities that promote relaxation and enjoyment, such as hobbies, spending time in nature, or engaging in creative outlets, can help alleviate stress and improve overall well-being.
Prioritize Self-Care
Taking care of oneself physically, emotionally, and mentally is important for individuals with fibromyositis. This can involve setting realistic expectations, pacing activities, and listening to one’s body to prevent overexertion and flare-ups. It is essential to balance activities and rest periods, ensuring that adequate time is given for recovery and relaxation. Additionally, seeking support from loved ones, joining support groups, or seeking professional counseling can provide valuable emotional support and coping strategies.
Improve Sleep Quality
Sleep disturbances are common in fibromyositis, and improving sleep quality can significantly impact overall well-being. Establishing a regular sleep routine, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing good sleep hygiene can contribute to better sleep. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, limiting caffeine and electronic device use before bed, and creating a calm and relaxing sleep environment. If sleep difficulties persist, consulting a healthcare professional for guidance and potential treatment options can be beneficial.
Seek Early Treatment for Pain and Symptoms
Prompt medical attention and early treatment can help manage symptoms and potentially prevent the progression of fibromyositis. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if experiencing persistent pain or symptoms that interfere with daily activities. The healthcare provider can evaluate the symptoms, provide appropriate treatment options, and develop a comprehensive management plan. Early intervention can lead to better symptom control and improved quality of life.
While these preventive strategies may not guarantee the prevention of fibromyositis, they can contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce the impact of symptoms. Each individual’s experience with fibromyositis is unique, and it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance. By adopting a proactive approach to self-care and making lifestyle choices that promote well-being, individuals can empower themselves in managing fibromyositis and optimizing their quality of life.
I need some more detailed paragraphs on the topic Treatment ofFibromyalgia, Medication,Physical therapy,Exercise,Alternative treatments . Please give me well details in each paragraph. use Fibromyositis instead of Fibromyalgia.
Fibromyalgia (Fibromyositis) Treatments:
Medication
Medication can play a significant role in managing the symptoms associated with fibromyositis. Various types of medications may be prescribed, depending on the individual’s specific symptoms and needs. Some common medications used in the treatment of fibromyositis include:
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help alleviate mild to moderate pain. In some cases, stronger prescription pain medications may be prescribed.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressant medications, such as duloxetine and amitriptyline, can help reduce pain and improve sleep quality. These medications work by altering the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain.
- Anticonvulsants: Medications typically used to treat seizures, such as gabapentin or pregabalin, have shown effectiveness in reducing pain and improving sleep in individuals with fibromyositis.
- Muscle relaxants: Muscle relaxant medications can help relieve muscle spasms and reduce pain associated with fibromyositis. These medications may be prescribed on a short-term basis for acute flare-ups.
- Sleep aids: In cases where sleep disturbances are significant, sleep aids may be prescribed to promote better sleep patterns and improve overall restfulness.
It’s important to note that medication is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and the effectiveness and potential side effects vary from person to person. A healthcare professional will evaluate the individual’s specific symptoms and medical history to determine the most appropriate medication options.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in managing fibromyositis by focusing on improving physical function, reducing pain, and increasing overall mobility. Physical therapists employ various techniques and exercises tailored to the individual’s needs. These may include:
- Stretching exercises: Gentle stretching exercises help improve flexibility, reduce muscle stiffness, and relieve pain.
- Strengthening exercises: Specific exercises target weak muscles, improve strength, and support better posture and joint stability.
- Aerobic exercises: Low-impact aerobic activities, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can improve cardiovascular fitness and help manage symptoms of fatigue.
- Manual therapy: Techniques like massage, myofascial release, and joint mobilization may be used to alleviate muscle tension and reduce pain.
- Education and self-management strategies: Physical therapists provide education on proper body mechanics, ergonomics, and self-care strategies that individuals can incorporate into their daily lives to manage symptoms more effectively.
Physical therapy aims to empower individuals with fibromyositis to take an active role in their own well-being and equip them with tools and techniques to manage their symptoms effectively.
Exercise
Regular exercise is an essential component of managing fibromyositis. While it may seem counterintuitive to engage in physical activity when experiencing pain and fatigue, exercise has been shown to have numerous benefits, including:
- Pain reduction: Regular exercise can help reduce pain sensitivity, improve muscle strength, and promote the release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers.
- Improved sleep: Engaging in exercise has been linked to better sleep quality, which is often disrupted in individuals with fibromyositis.
- Enhanced mood: Exercise stimulates the release of neurotransmitters that promote feelings of well-being and can help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Increased energy levels: While fatigue is a common symptom of fibromyositis, exercise can boost energy levels and improve overall stamina over time.
It’s important to start with low-impact activities and gradually increase intensity and duration as tolerated. Working with a healthcare professional or an exercise specialist who is familiar with fibromyositis can help develop an individualized exercise plan that takes into account the person’s specific limitations and goals.
Alternative Treatments
In addition to conventional treatments, some individuals with fibromyositis find relief and benefit from alternative therapies. While the effectiveness of these treatments varies from person to person, they may provide additional options for managing symptoms. Some alternative treatments that individuals may explore include:
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice involves the insertion of thin needles at specific points on the body to help alleviate pain and promote relaxation.
- Massage therapy: Massage can help reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and promote relaxation and pain relief.
- Yoga and tai chi: These mind-body practices combine gentle movements, stretching, and deep breathing exercises, which can help improve flexibility, reduce stress, and alleviate pain.
- Mindfulness meditation: Mindfulness techniques focus on cultivating awareness of the present moment, which can help individuals manage pain, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being.
- Herbal supplements: Some individuals may explore herbal supplements such as turmeric, ginger, or St. John’s Wort, although it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any supplements to ensure safety and potential interactions with other medications.
It’s essential to discuss alternative treatment options with a healthcare professional, as they can provide guidance, evaluate potential benefits, and ensure these treatments are used safely and in conjunction with other recommended therapies.
In summary, the treatment of fibromyositis involves a multidisciplinary approach aimed at managing symptoms, improving overall well-being, and promoting a better quality of life. Through a combination of medication, physical therapy, exercise, and alternative treatments, individuals can find strategies that work best for them, helping them manage pain, fatigue, and other symptoms associated with fibromyositis effectively. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop an individualized treatment plan tailored to one’s specific needs and goals.
Coping Strategies in Fibromyalgia (Fibromyositis):
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate the symptoms of fibromyositis, so implementing effective stress management techniques is crucial for individuals with the condition. Some strategies that can help reduce stress include:
- Identifying triggers: Recognizing and understanding the factors that contribute to stress can help individuals proactively address them. This may involve identifying specific situations, environments, or relationships that tend to cause stress and taking steps to minimize their impact.
- Practicing relaxation techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can promote relaxation and alleviate stress. These techniques help activate the body’s relaxation response, counteracting the effects of stress on the body.
- Engaging in stress-reducing activities: Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation can help individuals cope with stress. This may include hobbies, listening to music, spending time in nature, or pursuing creative outlets. Finding activities that provide a sense of calm and enjoyment can help reduce stress levels.
Self-Care
Self-care plays a crucial role in managing fibromyositis and promoting overall well-being. Taking care of oneself physically, emotionally, and mentally is essential for managing symptoms and maintaining a good quality of life. Some self-care practices that can be beneficial for individuals with fibromyositis include:
- Setting boundaries: Learning to say no and setting limits is important for avoiding overexertion and managing energy levels. It’s essential to prioritize activities and commitments that align with personal well-being.
- Practicing good sleep hygiene: Establishing a consistent sleep routine, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and engaging in relaxation techniques before bed can help improve sleep quality and reduce fatigue.
- Pacing activities: Breaking tasks into manageable segments and taking regular breaks can prevent overexertion and minimize symptom flare-ups. Finding a balance between activity and rest is crucial for managing energy levels effectively.
- Nurturing emotional well-being: Engaging in activities that promote emotional well-being, such as journaling, practicing gratitude, and seeking emotional support from loved ones or therapists, can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges of fibromyositis.
Support Groups
Participating in support groups can provide invaluable emotional support, validation, and information sharing for individuals with fibromyositis. Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with the condition can help reduce feelings of isolation and provide a sense of belonging. Support groups can offer a safe space for individuals to share experiences, exchange coping strategies, and receive encouragement and understanding.
Mindfulness Techniques
Mindfulness techniques can help individuals with fibromyositis develop a greater sense of awareness and presence, reducing stress and improving overall well-being. Some mindfulness practices that can be beneficial include:
- Meditation: Engaging in meditation practices, such as focused breathing or body scan meditation, can help individuals cultivate a state of calm and reduce stress levels. Regular meditation practice can enhance emotional resilience and improve overall mental well-being.
- Mindful movement: Practices such as yoga or tai chi combine gentle movements, stretching, and deep breathing exercises. These activities promote mindfulness, improve physical flexibility, and help alleviate stress and muscle tension.
- Staying present: Being fully present in the moment, paying attention to sensations, thoughts, and emotions without judgment, can help individuals cultivate a more compassionate and accepting attitude toward themselves and their experiences.
Incorporating mindfulness techniques into daily life can help individuals with fibromyositis navigate the challenges of the condition with greater ease and foster a greater sense of well-being.
In summary, individuals with fibromyositis can employ various coping strategies to manage their symptoms and enhance their overall well-being. By implementing stress management techniques, practicing self-care, participating in support groups, and incorporating mindfulness techniques, individuals can better navigate the challenges associated with fibromyositis and improve their quality of life. It is important for individuals to find a combination of coping strategies that work best for them and to seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and loved ones.
Fibromyalgia (Fibromyositis) Research:
Research studies focusing on fibromyositis aim to uncover the underlying mechanisms and factors contributing to the condition. Some areas of research include:
- Neurological Factors: Researchers have explored abnormalities in the central nervous system, such as altered pain processing, neurotransmitter imbalances, and neurochemical changes. Understanding these neurological factors can provide insights into the heightened sensitivity to pain experienced by individuals with fibromyositis.
- Genetic Factors: Studies have investigated genetic predispositions and variations that may increase the risk of developing fibromyositis. Identifying specific genes or genetic markers associated with the condition can contribute to improved diagnosis and personalized treatment approaches.
- Psychological Factors: Research has shown the significant impact of psychological factors, such as stress, trauma, and emotional well-being, on fibromyositis. Exploring the complex interplay between psychological factors and physical symptoms can help develop comprehensive treatment strategies.
- Immunological Factors: Investigations into the immune system’s dysregulation in individuals with fibromyositis have shed light on potential immune abnormalities and inflammatory processes. Understanding these immunological factors may lead to the development of targeted therapies.
- Treatment Interventions: Numerous studies have focused on evaluating the efficacy of various treatment modalities, including medication, physical therapy, exercise, and complementary therapies. These studies help determine the most effective approaches to symptom management and improvement in quality of life.
Advancing Knowledge and Treatment Options
Research studies on fibromyositis contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge and treatment options for individuals with the condition. They help healthcare professionals better understand the complexities of fibromyositis, leading to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans. Furthermore, research studies aid in the development of new medications, therapies, and interventions to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
The findings from research studies also contribute to the ongoing education and training of healthcare professionals, ensuring that they are equipped with the latest information and evidence-based practices to provide optimal care for individuals with fibromyositis.
Participating in Research Studies
Individuals with fibromyositis may have the opportunity to participate in research studies, which can have several benefits. Participation allows individuals to contribute to the advancement of knowledge, improve understanding of the condition, and potentially gain access to innovative treatments or interventions. However, it is important for individuals to carefully consider their involvement in research studies and discuss the risks, benefits, and expectations with healthcare professionals before making a decision.
In summary, research studies play a crucial role in enhancing the understanding and management of fibromyositis. Through investigations into neurological, genetic, psychological, and immunological factors, researchers continue to uncover valuable insights into the condition. The knowledge gained from these studies contributes to improved diagnosis, personalized treatment approaches, and the development of innovative interventions. By participating in research studies, individuals with fibromyositis can actively contribute to advancing medical knowledge and potentially benefit from cutting-edge therapies.
Explore Our More Articles
Conclusion:
Fibromyalgia, also known as fibromyositis, is a complex and chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, cognitive difficulties, and various other symptoms. It is a condition that significantly impacts the lives of those affected, requiring comprehensive management and support.
Throughout this overview, we have explored various aspects of fibromyalgia, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, prevention, treatment options, coping strategies, research studies, and more. While the exact cause of fibromyalgia remains unknown, research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors may contribute to its development. The diagnosis of fibromyalgia can be challenging due to the absence of specific diagnostic tests, but healthcare professionals rely on a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms and medical history to reach a diagnosis.
When it comes to managing fibromyalgia, a multimodal approach is often recommended. This includes a combination of medication, physical therapy, exercise, alternative treatments, stress management techniques, self-care practices, and support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and loved ones. Each individual may respond differently to various treatment options, so a personalized approach is essential.
Furthermore, individuals with fibromyalgia can benefit from adopting coping strategies that help reduce stress, promote self-care, engage in support networks, and incorporate mindfulness techniques. These strategies can improve overall well-being and enhance the ability to manage symptoms effectively.
Research studies focusing on fibromyalgia continue to contribute to the understanding of the condition, uncovering underlying mechanisms, identifying potential treatment interventions, and advancing medical knowledge. Participating in research studies can provide individuals with fibromyalgia the opportunity to contribute to scientific advancements and potentially access innovative therapies.
It is important for individuals with fibromyalgia to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive management plan tailored to their specific needs. By actively participating in their own care, individuals can take steps towards improving their quality of life and finding effective ways to manage the challenges posed by fibromyalgia.
In conclusion, fibromyalgia is a complex condition that requires a multidimensional approach to management. While it may present daily challenges, individuals with fibromyalgia can adopt various strategies to cope with symptoms, seek support from healthcare professionals and support networks, and actively engage in their own well-being. Ongoing research and advancements in understanding fibromyalgia offer hope for improved diagnosis, treatment options, and ultimately, a better quality of life for individuals living with this condition.
Q : 1. What are the common symptoms of fibromyalgia?
A : Fibromyalgia is characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, cognitive difficulties (“fibro fog”), headaches, irritable bowel syndrome, depression, and anxiety. Other symptoms may include stiffness, numbness or tingling sensations, sensitivity to noise, light, or temperature, and restless legs syndrome.
Q : 2. How is fibromyalgia diagnosed?
A : There is no specific test to diagnose fibromyalgia. Healthcare professionals rely on a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and physical examination to make a diagnosis. They may also consider the presence of specific tender points on the body. It is important to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms before reaching a diagnosis.
Q : 3. What are the available treatment options for fibromyalgia?
A : Treatment for fibromyalgia aims to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. It often involves a combination of medication, such as pain relievers and antidepressants, physical therapy, exercise, alternative treatments like acupuncture or massage, and lifestyle modifications. Each individual may respond differently to treatment, so a personalized approach is necessary.
Q : 4. Can fibromyalgia be prevented?
A : At present, there is no known way to prevent fibromyalgia. However, adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, getting regular exercise, practicing good sleep hygiene, and seeking early medical intervention for any associated conditions or injuries may help reduce the risk or severity of fibromyalgia symptoms.
Q : 5. Is fibromyalgia a lifelong condition?
A : Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition, meaning it typically lasts for a long time. However, the severity of symptoms can vary among individuals. With proper management and a combination of treatment approaches, many people with fibromyalgia are able to lead fulfilling lives and experience improvement in their symptoms.
More Related Links
Fibromyalgia |




